
Google’s latest case studies reveal both the promise and peril of automated advertising content
Table of Contents
- From Hype to Hard Numbers: Google’s AI Case-Study Trio
- Inside the Efficiency Engine: How Zepto, Ajio, and Zee5 Re-tooled Production
- When Dashboards Lie: The Hidden Gaps Behind the Metrics
- Automation’s Price Tag: Winners, Losers, and the Creative Economy
- Authenticity vs. Algorithm: Why Audiences Still Sense the Machine
- Early-Stage Tech, Late-Stage Expectations: A Reality Check for Marketers
- Hybrid Is the Future: Where Humans Add Irreplaceable Value
- Measuring What Matters: Beyond Click-Throughs to Long-Term Brand Health
- FAQ: AI Video Advertising
From Hype to Hard Numbers: Google’s AI Case-Study Trio
“Efficiency is easy to measure; authenticity is harder—and ultimately more expensive to fake.”
In August 2025, Google published a report that seemed to herald a new era in digital marketing. Three major Indian companies—quick-commerce platform Zepto, fashion retailer Ajio, and streaming service Zee5—had achieved remarkable results using Google’s AI-powered video creation tools.
The numbers were striking:
These case studies represent more than isolated success stories. They offer a window into how artificial intelligence is reshaping one of the economy’s most creativity-dependent sectors, with implications that extend far beyond marketing departments into questions of human creativity, economic disruption, and the future of work itself.
Inside the Efficiency Engine: How Zepto, Ajio, and Zee5 Re-tooled Production

“We’re not talking marginal gains; we’re talking orders-of-magnitude speed. What used to be a quarterly content calendar is now a lunch-break task.”
The three companies featured in Google’s report faced distinctly different challenges that AI marketing automation promised to solve.
Zepto: Quick Commerce at Lightning Speed
Zepto, operating in India’s hyper-competitive quick-commerce market, needed to scale marketing rapidly to capture growing consumer demand for rapid grocery delivery. Traditional video production—requiring coordination between photographers, editors, and creative teams—couldn’t match the velocity needed for their expansion1.
Google’s solution integrated the company’s Veo AI model, which transforms static product images into dynamic videos complete with music, motion graphics, and captions. The process that once took days or weeks could now be completed in minutes.
The results spoke directly to Zepto’s bottom line:
- App installation volumes doubled
- 11% greater efficiency in marketing spend1
Ajio: Fashion Content at Scale
Ajio faced a different but related challenge. With a catalog spanning 2.5 million individual fashion items, the Reliance Retail subsidiary couldn’t possibly create video content for more than a tiny fraction of its inventory using traditional methods.
Google’s AI video generation solution could generate over 100 social-media-friendly videos with voiceovers and product carousels in a single hour, drawing automatically from product images and descriptions in Google Merchant Centre1.
The fashion platform integrated Google’s Gemini model for text-to-speech capabilities, creating natural-sounding narration that could be customized for different demographics.
The business impact was measurable:
- Cross-selling and upselling improved by 80%
- 20% incremental conversions across YouTube Shorts and in-stream advertisements1
Zee5: Entertainment Industry Automation
Zee5’s challenge centered on creative fatigue—the streaming service’s wealth of content required constant trailer creation, but traditional editing processes created bottlenecks that limited marketing agility. Google’s Gemini-powered video editing tool allowed marketers to generate multiple trailer versions of varying lengths for different platforms using simple text prompts1.
The time savings were dramatic:
- Tasks that previously required 16 hours could be completed in under an hour
- Tripled the number of videos in campaigns
- Reduced both editing costs and time-to-market
- A/B testing confirmed that AI-generated trailers performed on par with manually edited versions1
“AI cut trailer production from sixteen hours to sixty minutes—but audiences could still feel the joins.”
When Dashboards Lie: The Hidden Gaps Behind the Metrics
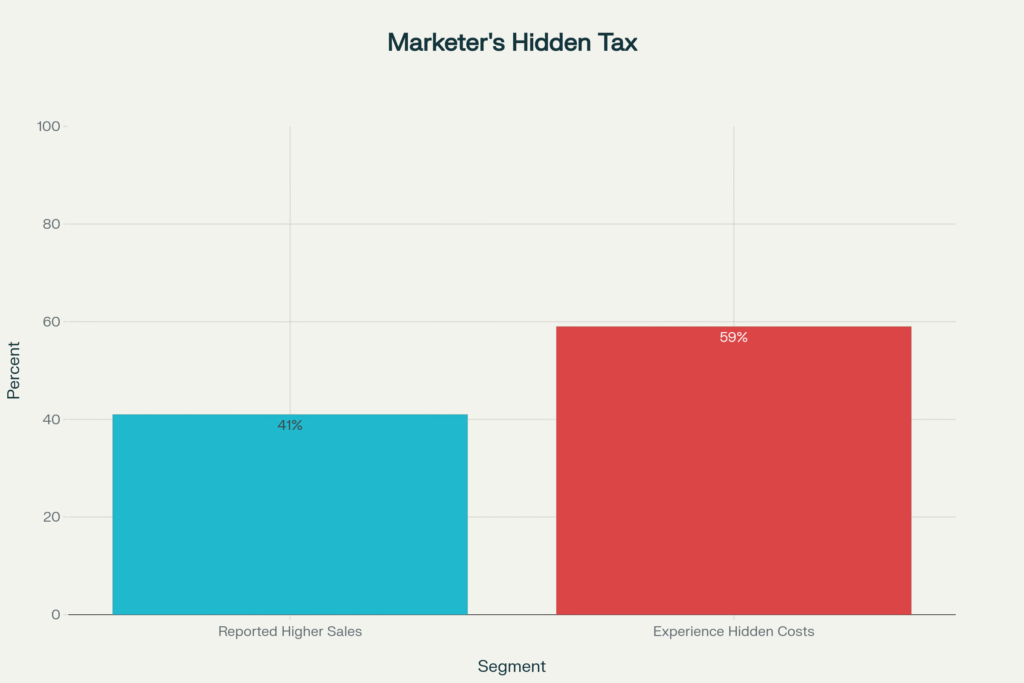
“Google’s success stories are spectacular, but they’re also curated. Real-world users report a reality that’s messier, glitchier, and far less automatic.”
While Google’s case studies paint an optimistic picture, user experiences with AI creative tools reveal significant gaps between marketing promises and practical implementation. Online communities dedicated to Google’s Veo video generation tool document persistent technical issues that contradict the seamless efficiency described in corporate case studies3.
The Technical Reality
Users report frequent system failures with generic “Something went wrong” error messages that prevent video generation entirely. Daily usage limits interrupt workflows unexpectedly, while identical prompts often produce wildly inconsistent results.
One detailed user complaint described the experience as dramatically inferior to promotional demonstrations, comparing the quality degradation to “switching from PlayStation 5 to PlayStation 2”3.
Implementation Gaps
These technical limitations extend beyond mere inconvenience. They suggest that current AI marketing tools remain far more brittle and context-dependent than their promotional materials indicate.
The success stories featured in Google’s report likely represent:
- Carefully curated implementations with significant human oversight
- Enterprise-level support not available to typical users
- Cherry-picked results rather than average performance
Missing Critical Data
The measurement gaps in Google’s analysis further complicate the picture. While the report provides impressive performance metrics, it omits crucial details about:
- Implementation costs beyond software licensing
- Failure rates and troubleshooting time
- Human resources required to achieve results
- Long-term performance sustainability data45
“Forty-one percent of marketers see higher sales from AI—but most still pay a hidden tax in troubleshooting and human oversight.”
Automation’s Price Tag: Winners, Losers, and the Creative Economy
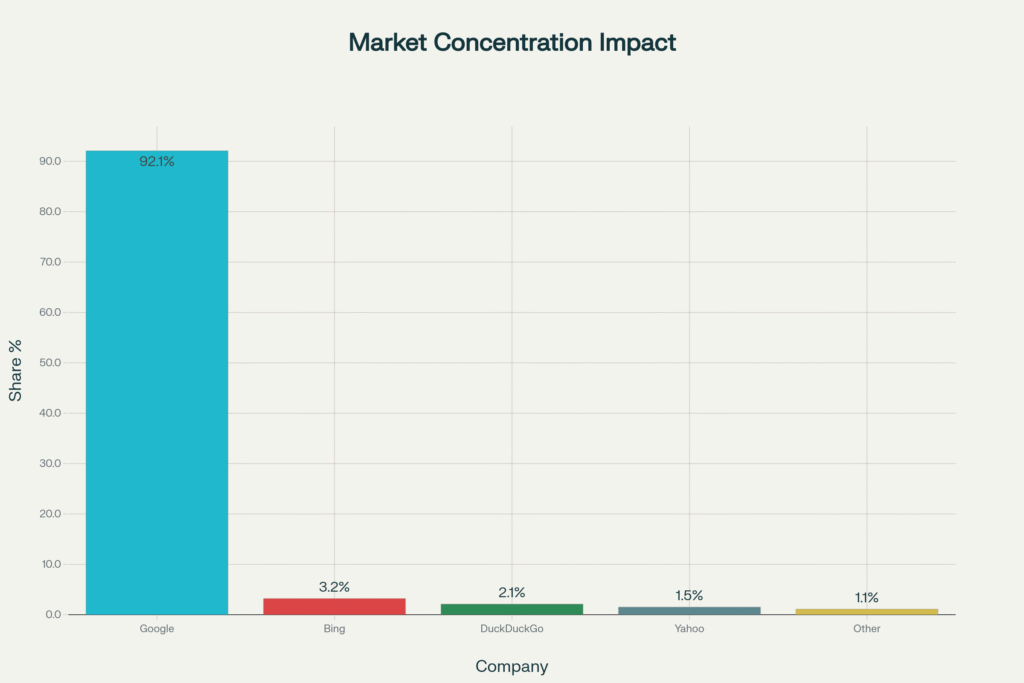
“Every minute saved in production is a minute lost for freelancers who once did that work. The efficiency dividend has a human cost.”
The shift toward AI-generated advertising content carries profound economic implications that extend far beyond the companies implementing these tools. Traditional advertising production supports complex ecosystems of freelance creative professionals—photographers, videographers, editors, voice actors, musicians, and graphic designers whose livelihoods depend on continued demand for human-created content.
The Displacement Reality
When companies like Zepto, Ajio, and Zee5 automate significant portions of their creative production, the immediate beneficiaries are clear: reduced costs, increased efficiency, and greater scale.
But the broader economic impact remains largely invisible in corporate success stories:
- Creative professionals who no longer receive commissions
- Production companies whose services become redundant
- Cultural institutions that depend on commercial creative work for sustainability6
The Training Data Paradox
This displacement creates a paradox that threatens the long-term viability of AI creative systems. Current AI models depend entirely on human-created content for their training data. If commercial incentives for human creativity diminish significantly, the cultural ecosystem that produces training material for future AI models could atrophy, creating a feedback loop that ultimately undermines the technology’s own foundation7.
“Without fresh human work feeding the datasets, the AI well eventually runs dry.”
Market Concentration Concerns
The concentration of AI creative capabilities in the hands of major technology companies adds another layer of concern. Google’s dominance in AI-powered advertising tools gives the company unprecedented influence over:
- Creative vocabulary available to brands
- Visual and narrative language of contemporary culture8
Authenticity vs. Algorithm: Why Audiences Still Sense the Machine

“Audiences tolerate polish; they resent pretense. The second they suspect a synthetic voice, trust erodes.”
Modern consumers have developed sophisticated abilities to detect artificially manufactured content, particularly among younger demographics who prize authenticity in brand communications. This creates a fundamental tension for AI-generated advertising: as these tools become more sophisticated at mimicking human creativity, they may actually become less effective at achieving the authentic connections that drive consumer engagement9.
The Uncanny Valley Effect
The streaming service Zee5’s experience illustrates this paradox perfectly. While their AI-generated trailers matched human-edited versions in quantitative metrics like click-through rates, qualitative surveys revealed lower scores for:
- Viewer satisfaction
- Brand perception
- Emotional connection1
Audiences could sense, even without being able to articulate why, that something was different about the algorithmically assembled content.
The Path Forward
This “uncanny valley” effect in marketing content suggests that the future of AI in advertising may not lie in replacing human creativity but in augmenting it. The most successful implementations may be those that:
- Embrace rather than hide their artificial nature
- Use technological capabilities to expand rather than substitute for human insight
- Maintain cultural understanding10
“When algorithms supply the creative, the real scarcity shifts from content to cultural intuition.”
Early-Stage Tech, Late-Stage Expectations: A Reality Check for Marketers
“Generative models are brilliant plagiarists—they remix, they don’t originate. That matters when your brand equity hinges on originality.”
The adoption of AI creative tools follows patterns visible across other industries experiencing automation. Early implementations focus on efficiency gains and cost reduction, often in areas where human creativity was already constrained by budget or time limitations. Success stories emphasize quantitative improvements while downplaying qualitative trade-offs11.
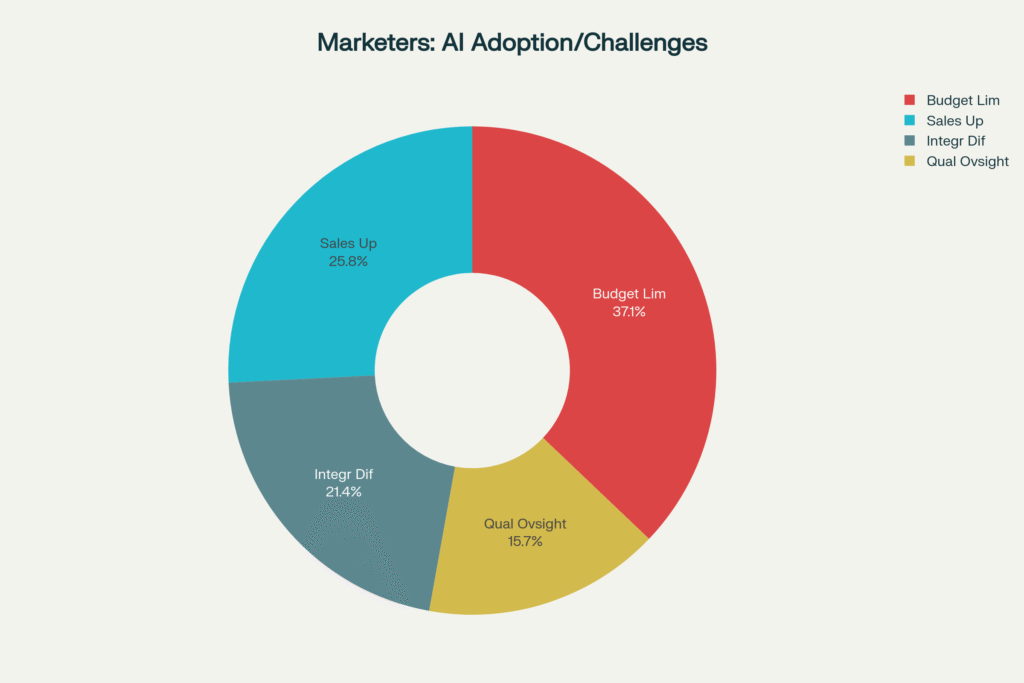
Market Reality Check
Marketing automation trends indicate that 41% of marketers report increased sales from AI integration, but many struggle with implementation challenges including:
- Budget constraints
- Integration difficulties with existing workflows
- Quality control issues requiring significant human oversight1213
These patterns suggest that current AI creative tools represent evolutionary rather than revolutionary change—valuable for specific use cases but far from the comprehensive transformation suggested by promotional materials.
Competitive Landscape Analysis
The competitive landscape reveals similar limitations. While Google promotes its Veo and Gemini integration, competitors like AdCreative.ai claim superior performance metrics, including:
- 2x higher click-through rates
- 50% return-on-ad-spend improvements14
The proliferation of similar claims across different platforms suggests that no single solution has achieved decisive technological advantage, indicating the technology remains in early development stages.
“The same technology that democratizes video ads can also homogenize them, flattening brand voices into a single algorithmic accent.”
Hybrid Is the Future: Where Humans Add Irreplaceable Value
“The sweet spot is not man versus machine but man with machine—automation for repetition, people for resonance.”
The broader cultural implications of automated creativity extend beyond immediate business applications. If machines can generate competent creative content at industrial scale, fundamental questions arise about:
- Human uniqueness
- The value of artistic labor
- Economic structures that traditionally support creative communities7
The Homogenization Risk
The risk may not be that machines will produce inferior creative content—though current evidence suggests significant limitations—but that they will produce homogenized content reflecting the biases and assumptions embedded in their training data and algorithms.
A creative landscape dominated by AI models trained on similar datasets could result in diminished cultural diversity and creative expression8.
Human Creative Advantages
Current AI creative tools excel at pattern recognition and stylistic mimicry but struggle with cultural intuition that allows human creators to:
- Subvert expectations
- Challenge conventions
- Tap into unconscious emotional responses
This limitation suggests that while AI can automate certain aspects of creative production, it cannot replicate the kind of cultural commentary and creative risk-taking that produces genuinely innovative advertising15.
The Sustainable Path Forward
The trajectory of AI in advertising will likely be determined by how successfully companies navigate the complex interplay between:
- Efficiency and authenticity
- Automation and human insight
- Technological capability and cultural understanding
Current evidence suggests that the most effective implementations treat AI as a tool for augmenting rather than replacing human creativity10.
Google continues refining its AI creative tools, addressing technical limitations while expanding available content types and creative styles. However, the fundamental challenges—inconsistent quality, limited cultural understanding, and the authenticity paradox—represent deeper obstacles than software updates can easily resolve3.
The most sustainable path forward may involve hybrid approaches that:
- Leverage AI’s efficiency advantages
- Preserve human oversight for strategic creative decisions
- Maintain cultural interpretation and brand voice development
This suggests a future where AI handles routine creative tasks while humans focus on higher-level creative strategy and cultural insight16.
Measuring What Matters: Beyond Click-Throughs to Long-Term Brand Health
“Efficiency is easy to measure; authenticity is harder—and ultimately more expensive to fake.”
Evaluating the success of AI creative tools requires metrics that extend beyond immediate performance indicators. While Google’s case studies demonstrate impressive efficiency gains and conversion improvements, they provide limited insight into:
- Long-term sustainability
- Creative quality evolution
- Audience reception patterns4
Comprehensive Assessment Framework
Comprehensive assessment would include:
- Failure rates alongside successes
- Implementation costs beyond software licensing
- Qualitative measures of creative effectiveness versus human-generated alternatives
- Long-term brand perception impact5
Without this broader context, current success stories may represent selective reporting that obscures significant limitations and implementation challenges.
Independent Validation Gap
The absence of independent validation further complicates evaluation. All three case studies featured in Google’s report involve direct partnerships with Google, creating potential bias in both:
- Implementation support
- Results reporting
Independent studies comparing different AI creative platforms and measuring long-term performance would provide more reliable insights into the technology’s actual capabilities and limitations17.
FAQ: AI Video Advertising
Q: Does AI video advertising always outperform human-made ads?
A: No. AI excels at speed and scalability, but human-edited content often scores higher on emotional resonance and brand perception. Zee5’s experience showed AI trailers matched click-through rates but scored lower on viewer satisfaction.
Q: What’s the biggest hidden cost of AI creative tools?
A: Human oversight—time spent troubleshooting, curating outputs, and safeguarding brand voice. Most implementations require significant quality control despite promises of full automation.
Q: How can brands keep AI content feeling authentic?
A: Combine machine-generated drafts with human final edits, disclose AI use transparently, and prioritize narrative coherence over sheer volume. The most successful approaches treat AI as augmentation, not replacement.
Q: Are AI creative tools reliable enough for enterprise use?
A: Current tools show promise but remain brittle. Users report frequent failures, inconsistent quality, and daily usage limits that interrupt workflows. Enterprise success stories likely involve significant human oversight not reflected in promotional materials.
Q: Will AI creative tools eliminate creative jobs?
A: They will likely transform rather than eliminate them. While some routine tasks become automated, demand may increase for creative professionals who can effectively integrate AI capabilities with human insight and cultural understanding.
The Road Ahead
The current state of AI creative tools represents a transition moment rather than a definitive transformation. The technology demonstrates clear capabilities for specific use cases—particularly high-volume, template-based creative production—while revealing significant limitations in areas requiring cultural insight, creative risk-taking, and authentic brand voice development.
Realistic Expectation Setting
Companies considering AI creative implementation face the challenge of realistic expectation setting. The technology can deliver meaningful efficiency gains and cost reductions for appropriate applications, but it cannot replace human creativity wholesale.
Success requires:
- Understanding both capabilities and limitations
- Developing workflows that leverage AI’s strengths
- Preserving human creative input where it adds unique value
Industry Evolution
The broader implications for creative industries remain uncertain. While AI tools may displace some traditional creative roles, they may also create new opportunities for creative professionals who can effectively integrate AI capabilities with human insight and cultural understanding.
The ultimate impact will depend on how successfully the industry navigates the balance between technological efficiency and human creativity.
Final Assessment
The AI creative revolution, as Google’s case studies illustrate, is both more promising and more limited than its most enthusiastic proponents suggest. Understanding this complexity—embracing both the opportunities and acknowledging the constraints—represents the key to successfully navigating the evolving landscape of algorithmic creativity in marketing and beyond.
This analysis is based on publicly available case studies, user reports, and industry research. Performance metrics cited are drawn from Google’s published materials and should be evaluated within the context of potential selection bias inherent in corporate success stories.
Sources:
1 Google Think with Google – AI Video Ad Creatives India
2 Think with Google APAC – AI Video Ad Creatives
3 Reddit – Veo 3 Video Generation Issues
4 Innovify – Measuring ROI of Generative AI in Marketing
5 Hurree – Measuring ROI of AI in Marketing
6 Creatopy – Creative Automation Challenges
7 AOKI Studio – Arguments Against AI in Creative Fields
8 Economic Times – Indian Advertising Cultural Stereotypes
9 Brand Equity – Tira Beauty Universal Tension Ad
10 Xponent21 – Managing AI Limitations
11 Eacel – Performance Marketing Trends
12 Bannerflow – AI Marketing 2025 Trends
13 Saffron Edge – Marketing Automation Trends
14 AdCreative.ai – ROI of AI-Generated Ad Creatives
15 Lumenalta – AI Limitations
16 Braze – AI Marketing Automation
17 Jervex – Measuring True Value of AI in Marketing
